capítulo 3: Nutrición
95
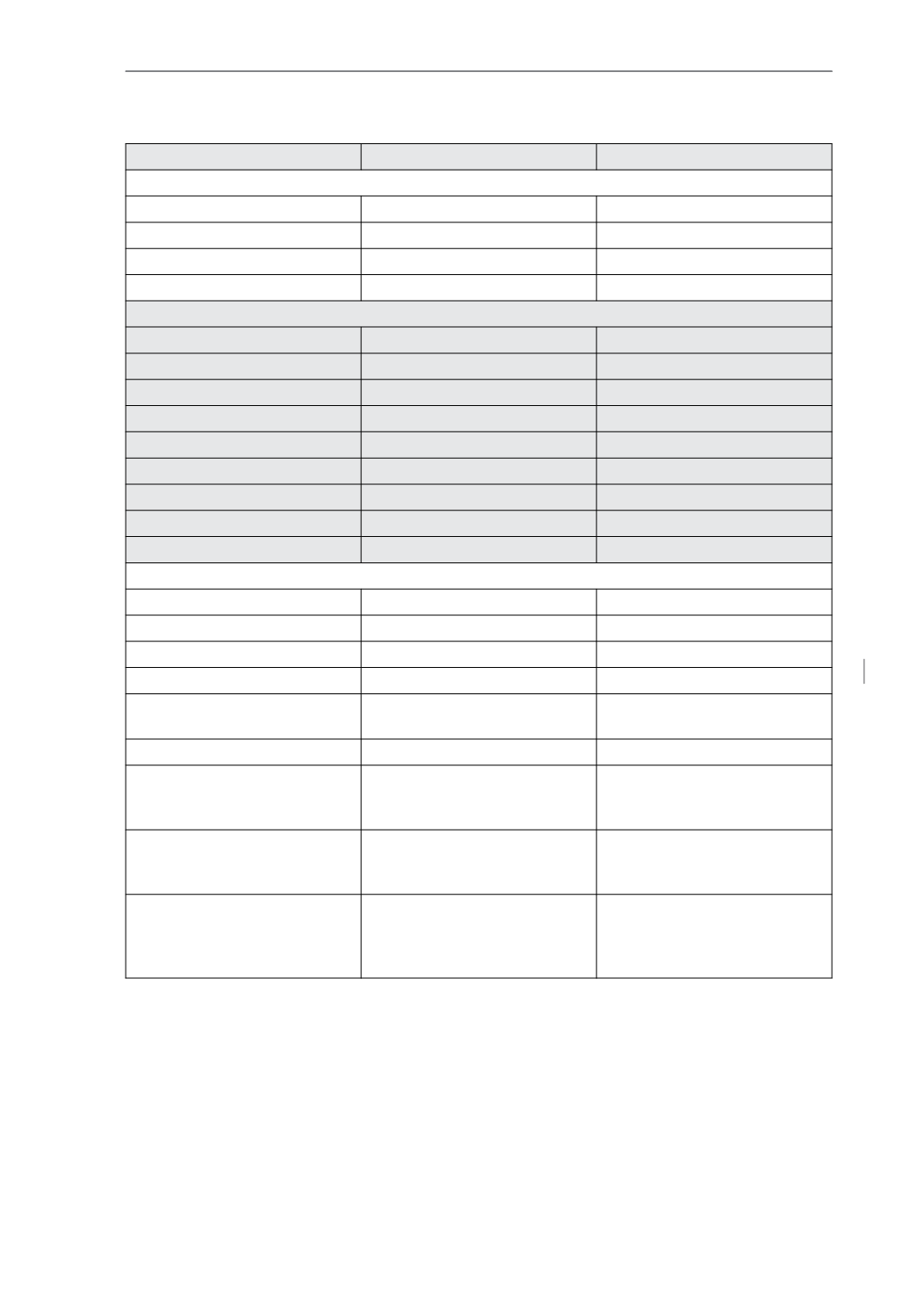
Tabla 4. Requerimientos de electrolitos, Vitaminas y Micronutrientes en NP:
lactantes y escolares
Infants
Children
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin A
a
150–300 mcg/kg/d
150 mcg/d
Vitamin D
0.8 mcg/32 IU per kg/d
10 mcg/400 IU per d
Vitamin E
2.8–3.5 mg/kg/d
7 mg/d
Vitamin K
10 mcg/kg/d
200 mcg/d
Water-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamin B
1
(thiamine)
0.35–0.5 mg/kg/d
1.2 mg/d
Vitamin B
2
(riboflavin)
0.15–0.2 mg/kg/d
1.4 mg/d
Vitamin B
3
(niacin)
4.0–6.8 mg/kg/d
17 mg/d
Vitamin B
5
(pantothenic acid)
1–2 mg/kg/d
5 mg/d
Vitamin B
6
(pyridoxine)
0.15–0.2 mg/kg/d
1 mg/d
Vitamin B
12
(cyanocobalamin)
0.3 mcg/kg/d
1 mcg/d
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
15–25 mg/kg/d
80 mg/d
Folate
56 mcg/kg/d
140 mcg/d
Biotin
5–8 mcg/kg/d
20 mcg/d
Trace Elements
Copper
20 mcg/kg/d (no max stated)
b
20 mcg/kg/d (500 mcg/d max
c,d
)
b
Chromium
0.2 mcg/kg/d (max 5 mcg/d)
e
0.2 mcg/kg/d (max 5 mcg/d
c
)
e
Fluoride
No recommendations
No recommendations
Iodine
1 mcg/d
f
1 mcg/d
f
Iron
Premature: 200 mcg/kg/d
f
Infant: 50–100 mcg/kg/d
f
50–100 mcg/kg/d
f
Manganese
1 mcg/kg/d (max 50 mcg/d
c
)
1 mcg/kg/d (max 50 mcg/d
c
)
Molybdenum
Premature: 1 mcg/kg/d
Infant: 0.25 mcg/kg/d
(max 5 mcg/d
c
)
0.25 mcg/kg/d (max 5 mcg/d
c
)
Selenium
Premature: 2–3 mcg/kg/d
Infant: 1–3 mcg/kg/d
(no max stated)
1–3 mcg/kg/d
(100 mcg/d max
c,d
)
Zinc
Premature: 450–500 mcg/kg/d
Infants < 3 mo: 250 mcg/kg/d
Infants > 3 mo: 50 mcg/kg/d
(max 5000 mcg/d)
50 mcg/kg/d (max 5000 mcg/d
c
)
IU, International Unit; max, maximum; PN, parenteral nutrition.
a
1 mcg/kg RAE (retinol activity equivalent) = 1 mcg/kg retinol.
b
Authors recommend monitoring plasma copper and ceruloplasmin concentrations in long-term PN patients
and patients with burns or cholestasis with appropriate adjustment of doses as needed.
c
Refers to maximum dose for routine supplementation; however, higher doses may be indicated in patients
with established deficiency or increased requirements.
d
Maximum dose was not specified in above reference but is included in this table as the maximum dose based
on the recommended adult dose.
e
Authors state that chromium contaminates in PN products satisfies requirements; therefore, additional
supplementation is unnecessary.
f
Not currently added to PN in U.S.
Vanek V, et al. Nutr Clin Pract 2012;27:440-91. *Nota: los límites superiores de los rangos son para condicio-
nes clínicas que se presentan con aumento de las pérdidas.